Nickel is one of the most versatile metals currently available. It is resistant to high temperatures, corrosion, and oxidation, among other features, making it a key component in a wide variety of everyday objects. Nevertheless, one thing this essential metal is not impervious to, as everyone has learned over the last couple of years, is global supply chain disruptions. This has become particularly apparent today in light of the Ukraine-Russia War and the international sanctions imposed on Russia as a result. World events today have therefore effectively cut off one of the leading sources of nickel to the global market which has resulted in a spike in prices of nearly 400% in a single day on the London Metal Exchange before trading was suspended. These record surges have drastically impacted the global nickel market, and by extension a wide array of related industries around the world.
By Isadora Henriques, Mechanical Engineer – Teadit
Discovered in the 18th century, nickel is one of the key elements that allow us to live and prosper in the modern world. In its pure form, it is a silvery-white metal that has noticeably attractive properties such as toughness, resistance to both corrosion and heat, and high melting and boiling points. Belonging to the transition metals, it also stands out for its relatively high electrical and thermal conductivity properties.
Its most important quality is, perhaps, its ability to alloy with other metals to create remarkable materials. There are thousands of nickel-based metals and alloys used regularly within major industrial segments. For instance, roughly 65% of its world production is utilized in the manufacturing of stainless steel. At its peak in 2019 there were over 52,000,000 tons of stainless steel produced globally and, prior to the pandemic, that number had been steadily increasing year over year for a decade.
Nickel Prices Exploding Worldwide
The current Ukraine-Russia War has drastically impacted the stock market and global economy that has already been struggling to recover from the pandemic. The sudden increase in the price of commodities has drawn attention, especially nickel prices. Russia is the world’s third-largest producer of nickel overall and the largest of primary nickel products. Its ability to export goods and participate in world trade has however been dramatically hindered due to continuing sanctions.
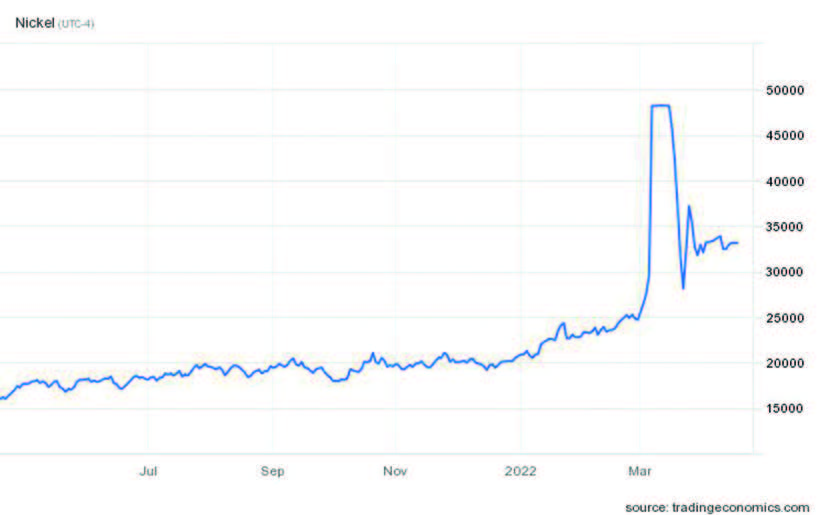
In March 2022, the world’s largest metal exchange suspended nickel trading after the price rapidly rose within two days and surpassed USD $100,000 per ton. Just a few days earlier it had been trading at roughly USD $25,000 per ton. Fears over shortages and availability of the material, led to the drastic rise in prices and have already begun leading to delays in production lines and the delivery of nickel-based materials. According to the financial group Goldman Sachs, nickel stocks are estimated to show deficits of 30,000 tons.
Nickel-Based Solutions
Nickel is a valuable material to the global sealing industry. It is present in many valves and fittings, as well as most metallic and semi-metallic gaskets, such as the ones made from stainless steel or Inconel®. The well-known SAE 304, for instance, has a minimum of 8% nickel, SAE 316 has 10%, and Inconel® 600 can have more than 72% in its compositions. These components are critical in many industrial manufacturing systems.
Nickel-based sealing solutions provide the required resilience and performance needed by most end users. They offer long life in severe environments while meeting strict requirements, which reduces maintenance and replacement costs, as well as unplanned down-time and loss of production. These products are commonly employed to withstand high temperature, high pressure, oxidation, and corrosion. They can also have additional features, such as controlled thermal expansion, electrical resistance, and magnetic characteristics. Other benefits may include good dimensional stability, compression and elastic recovery properties, mechanical strength, ductility and hardness, all of which are simple to optimize to enhance sealing and performance properties. High nickel alloy wire mesh is also a common component of most low emission compression packings that many valve manufacturers and end-users rely on to meet their fugitive emission requirements. All of these features mean that nickel-based products will continue to be relied on in a wide variety of industrial processing environments.

Nickel Price Surges Effect on Industry
Industries, in general, are feeling the effects of price increases related to the costs of raw materials and commodities. Again, it is beneficial to use the example of stainless steel prices. Even though nickel only makes a small percentage (between 8 to 12%) of stainless steel in mass, it constitutes up to 60% of the cost. That means that prices of both materials in the market typically follow the same trends.
If the nickel market remains unstable and at a record high prices, the industry will inevitably see drastic increases in the cost of stainless steel valves, fittings, seals, gaskets, etc. This poses a number of challenges for manufacturers and end-users alike. High costs of raw materials will impact production and inventory, as the cost of finished goods continue to climb. As a result, project planning and budgets will have to account for this instability.
Alternative Solutions
It is still uncertain of how long this instability will last or the future of availability. One benefit of these types of disruptions is that necessity breeds innovation, as industry inevitably seeks out alternatives to meet existing needs.
Teadit, for example, has recently developed a low emission valve packing that replaces the traditional Inconnel high-nickel alloy mesh with an alternative mesh made from ultra-high strength expanded PTFE threads. This non-metallic technology boasts nearly 2x the strength of its metallic counterpart and, in testing, and offers excellent emissions/leakage performance from a low-e packing.
Another example of alternatives being sought out are duplex and super duplex. Both materials offer several benefits for the industry thanks to their enhanced metallurgical structure, including: high resistance to corrosion, high strength, and good weldability. Although they both do contain nickel in their composition, it is less than 10% of the overall makeup.
Regardless of what the future may hold for nickel and other raw materials, recent events have shown that former stalwarts like supply chain reliability and cost stability are significantly more vulnerable to disruption than was ever realized. Though this lesson has not been easily learned, the challenges the industry has faced over the last few years and those we continue to face even today can, have, and likely will continue to lead to improvements, innovations, and redundancies that give us reason to be hopeful and encouraged.



