As larger gas turbine plants purchase hundreds of thousands of dollars of valves and support annually, the valve market is showing positive signs of increased demand as well as positive, steady growth.
By Robert McIlvaine, CEO – McIlvaine Company

The valve market for gas turbines is expanding at 6% per year. Thanks to low-cost LNG, worldwide access to fuel for gas turbines will be easily available.
Due to environmental needs and demand, the existing plants that are open cycle are being converted to combine cycle. Gas turbine plants older than 10 years are being upgraded to higher efficiency.
Wind and solar are popular choices only where conditions warrant and there is ample space. This leaves parts of the world with the need for a more reliable source of power. Combining reliable gas turbine power plants with solar and wind is an increasingly popular approach.
Open Cycle Gas Turbine Plants:
- Simpler Valve Requirements: Open cycle gas turbine (OCGT) plants generally have simpler valve requirements compared to combined cycle gas turbine (CCGT) plants. This is because they have fewer process streams and operate with less complex heat recovery systems.
- Fuel Gas Valves: These are critical for controlling the flow of natural gas or other fuels to the gas turbine combustor. They need to be fast-acting and reliable for starting, stopping, and modulating the turbine’s output. Safety shutoff valves (SSVs) are essential for quickly cutting off fuel supply in emergency situations.
- Air Inlet Valves: Open cycle gas turbine plants have inlet valves to control the flow of air into the compressor. These valves may be used for anti-icing or for flow control during startup and shutdown.
- Blow-Off Valves: Some OCGT plants may have blow-off valves to vent excess compressed air during startup or shutdown.
- Water Injection Valves (if applicable): If the OCGT plant uses water injection for NOx control, there will be valves to control the flow of water into the combustor.
Combined Cycle Gas Turbine Plants:
Combined cycle gas turbine plants incorporate a heat recovery steam generator (HRSG) to capture waste heat from the gas turbine exhaust and use it to generate steam, which drives a steam turbine. This added complexity significantly increases the valve requirements.
- All OCGT Valves plus CCGT plants have all the valve requirements of OCGT plants, plus additional valves related to the steam cycle.
- HRSG Valves: The HRSG requires a wide variety of valves, including:
- Feedwater Valves: Control the flow of feedwater into the HRSG.
- Steam Valves: Control the flow of steam from the HRSG to the steam turbine. These include main steam stop valves, control valves, and reheat steam valves.
- Blowdown Valves: Used to remove accumulated solids and impurities from the HRSG.
- Safety Valves: Protect the HRSG from overpressure.
- Drain Valves: Used to drain the HRSG during shutdown.
- Steam Turbine Valves: The steam turbine also requires a variety of valves, including:
- Main Steam Stop Valve: Isolates the steam turbine from the steam supply.
- Control Valves: Regulate the flow of steam into the turbine to control its speed and power output.
- Extraction Valves: In some CCGT plants, steam is extracted from the steam turbine for process heating or other uses. Extraction valves control the flow of this steam.
- Condenser Valves: Control the flow of cooling water to the condenser, which condenses the exhaust steam from the turbine.
- Water Chemistry Control Valves: CCGT plants require precise control of water chemistry to prevent corrosion and scaling in the HRSG and steam turbine. A variety of valves are used to inject chemicals and control pH.
- Bypass Valves: CCGT plants often have bypass valves that allow the gas turbine to operate even when the steam turbine is offline. These valves divert the gas turbine exhaust directly to the atmosphere.
The U.S. represents close to 25% of the total gas turbine valve market. There are 500,000 MW of gas turbines installed in the U.S. with 60% being combined cycle. The retrofit and replacement markets are larger than the market for new plants despite steady growth of gas turbine capacity. The total market in the U.S. for 2025 is USD$595,680,000.
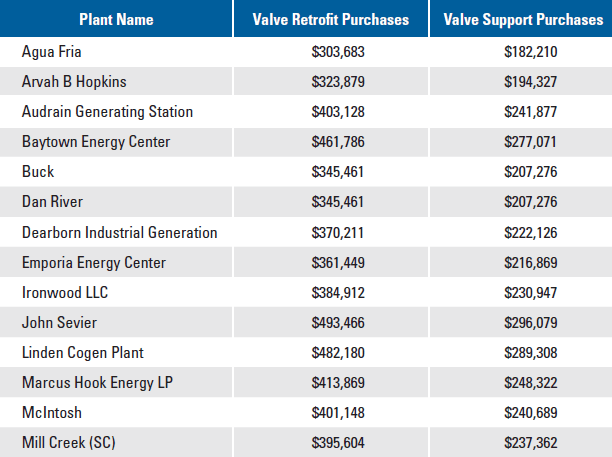
Larger gas turbine plants purchase hundreds of thousands of dollars of valves and support including parts, service, remote O&M, and support.
The valve market for gas turbine power plants will continue to rise at a rate greater than GDP. In addition to the valves required for the turbine operation itself, there are sets of valves required for the water purification and quantity used in these operations as well. Also, many operators are choosing zero liquid discharge—if for no other reason—than to avoid expensive environmental permits to discharge water.


